
Aims and Objectives
Introduction of world economy is a professional required course for international economy and trade major.The purpose of the course is to grasp the basic theory of the world economy, understand the laws of the world economy, development and change, especially in the new situation and problems in the process of economic globalization, such as global economic imbalance, the construction of new international economic order, population, resources, environmental and sustainable development, economic crisis, international financial supervision.
Learning Outcomes
By the end of the Module students will be able to:
LO1:Analysis of the global economic structures and processes in the world.
LO2:Understand the volatility of financial and currency markets has an impact on the real sphere of the economy ,and a crisis may jump from one country to another
LO3:Understand important issue is how financial crises can be prevented and what role the IMF should play
LO4:Analysis of regional dimension of the world economy , namely at developing countries and the new market economies ( transformation countries )
LO5:It also analyzes approaches to regional integration in the world including the European Union .The course also addresses potential conflicts between the national interest and global concerns. This relates to national protectionism versus free trade . It also refers to the concept of locational competition which means that the immobile factors of production , that is labor , compete for the mobile factors.
Module Outline (brief description of content)
The course of the world economy provides an analysis of the global economic structures and processes in the world . It looks at the economy of the planet Earth as if the world were observed from outer space . In a time when the communication system is organized globally , when we can communicate from Buenos Aires to Kiel over the Internet and when huge quantities of data can be interchanged between Cambridge and Hangzhou , when CNN broadcasts news worldwide , when transport costs are becoming less and less important and when more and more people are becoming accustomed to finding their jobs in all parts of the world , such a world view of the economic processes and structures appears to be imperative .
The volatility of financial and currency markets has an impact on the real sphere of the economy ,and a crisis may jump from one country to another . An important issue is how financial crises can be prevented and what role the IMF should play .In a further step , the course looks at the regional dimension of the world economy , namely at developing countries and the new market economies ( transformation countries ) . It also analyzes approaches to regional integration in the world including the European Union .The course also addresses potential conflicts between the national interest and global concerns.This relates to national protectionism versus free trade . It also refers to the concept of locational competition which means that the immobile factors of production , that is labor , compete for the mobile factors.
Teaching and Learning Methods
Teaching methods and requirements: The theory of this course is mainly teaching, and a large number of empirical cases are added for teaching.In terms of learning, students should in addition to cooperate with the requirements of teachers to complete the basic teaching, but also should read a large number of books and literature, to write reading notes according to the reading catalogue.
Learning methods and requirements: Students need to use about 30 minutes before each class to read their learned content and the literature and reading books shared by teachers.After the end of the course, according to the content, the teacher arranged the content of the group, each time is more than half an hour.
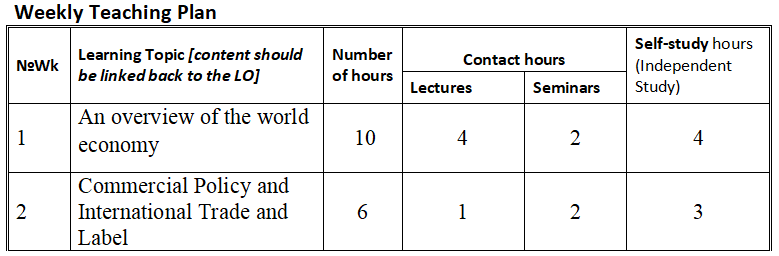
Weekly Programme Content
Week 1. Topic:Over view of World Economy
1.An Introduction to the world economy
2..International Economic Institutions(The IMF, the World Bank, and the WTO)
3.Understand the main existed forms in difference countries,for example,US.European.UK.Japan.
4.International Economic Institutions(The Role of International Economic Institutions;Criticism of International Institutions)
Week 2. Topic:Commercial Policy and International Trade and Label
1.Commercial Policy(Commercial Policy and Jobs;Protection in the European Union, Japan, and the United States)
2.Commercial Policy(Why Nations Protect Their Industries;The Politics of Protection in the United States)
3.International Trade and Labor and Environmental Standards(Income and Standards;Labor Standards)
4.International Trade and Labor and Environmental Standards(Trade and the Environment;Alternatives to Trade Measures)
Assessment
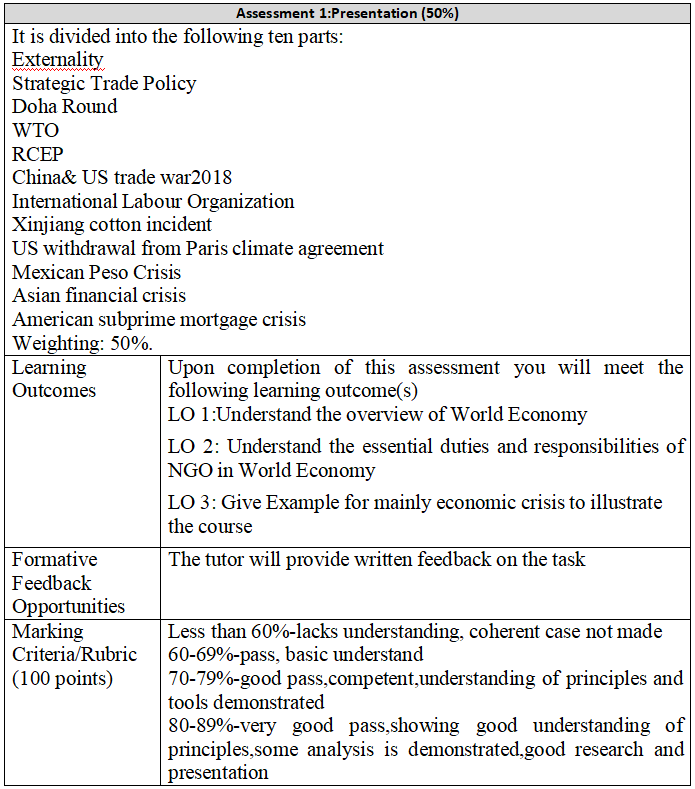
Assessment 1: Group project: the whole class is divided into 10 groups with 3-4 students in each group to find relevant cases and explain the contents. (100 point, worth 40% of module mark)
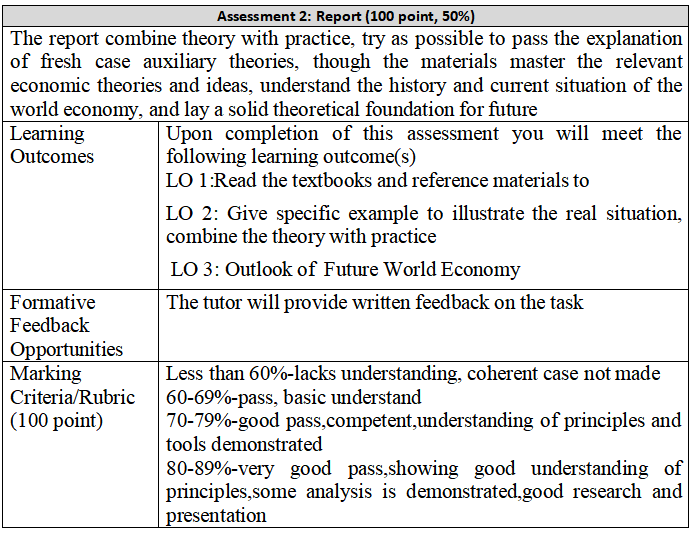
Assessment 2:Report, (worth 50% of module mark)
Reading List
Required Read (Read All):
1.《The World Economy》,Horst Siebert,1999,London and New York ,ISBN:0415217253
2.World Economics(Fourth Edition).James Gerber.China Renmin University Press,2008.
Select reading (select the relevant sections):
1.High heights: Battle of World Economy (I)
2.The housing bubble and the financial crisis,Dean Baker,real-world economics review, issue no. 46,2008
Program resource recommendation
1.A World Bank Group Flagship Report 30th anniversary edition Global Economic Prospects JUNE 2021
https://openknowledge.worldbank.org/bitstream/handle/10986/35647/9781464816659.pdf
2.The Impact of RCEP on Chinese Regional Economy From Global Value Chains Perspective,Lingling ZHOU,2021.
https://www.gtap.agecon.purdue.edu/resources/download/10412.pdf
3.World Trade Organization: Overview and Future Direction
https://sgp.fas.org/crs/row/R45417.pdf
4.WORLD TRADE ORGANISATION (WTO) AND ITS ROLE IN INTERNATIONAL TRADE
https://www.uwsp.edu/forestry/StuJournals/Documents/IRM/kaberia.pdf
5.Beyond Comparative Advantage
(1)the rising of strong countries
https://www.bilibili.com/bangumi/play/ss38207/?from=search&seid=16073463614039652391
6.International Trade and Labor and Environmental Standards
(1)Environmental standards and labor productivity: Understanding the mechanisms that sustain sustainability,11 September 2012,Magali A. Delmas, Sanja Pekovic
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/job.1827
(2)FUNDAMENTAL PRINCIPLES OF SAFETY - International Labour Organization
www.ilo.org/.../public/@dgreports/@dcomm/@publ/documents/publication/wcms_093550.pdf
7.International Financial Crisis
(1)The Secret History of Wall Street (Modern Finance)
http://v.ku6.com/show/g2qYzoljqgm_t6gghc9GgQ...html
(2)Basel New Capital Agreement
http://news.xinhuanet.com/video/2009-08/21/content_11920089.htm
(3)Princes of the Yen_ Central Bank Truth Documentary,
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=p5Ac7ap_MAY
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV14C4y1W7TX?from=search&seid=3574502608899801086
8.The European Union
(1)The European Union: Ongoing Challenges and Future Prospects,2018
https://sgp.fas.org/crs/row/R44249.pdf
9.Export-Oriented Growth in East Asia
(1)Export-Led Growth in East Asia: Lessons for Europe’s Transition Economies,2002
https://openresearch-repository.anu.edu.au/bitstream/1885/40110/3/kokko.pdf
上一篇:Investment Bank University of Sanya CHEN XIAOXIN
下一篇:Case Study Teaching Method in Western Economics University of Sanya XU FEI





